AIR PRODUCT
GLOSSARY
Use our Air Powered Product Glossary to enhance your understanding of the terminology associated with our air powered products.
Air Product Glossary
- Atmosphere Explosibles (ATEX): A European Directive concerning equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres. Hoists and Trolleys with ATEX ratings have spark-resistant features.
- Bumpers: A device for reducing horizontal impact when a moving crane or trolley reaches the end of its permitted travel, or when two moving cranes or trolleys come into contact. This device may be attached to the bridge, trolley, or runway stop. Also referred to as buffers.
- Capacity: The maximum rated load a hoist is designed to lift. Also referred to as Working Load Limit (WLL) or Safe Working Load (SWL).
- Chain Container: Container that holds the ‘no-load’ side of the load chain. Can be made of canvas, plastic, or steel.
- Chain Fall Lines: The number of lines of chain between the hoist body and bottom hook. Also referred to as “reaves”, “falls”, or “parts”.
- Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM): The volume of air that flows through the hoist or trolley at full speed. For hoists and trolleys, it is imperative that the air compressor and compressed air system can flow at least this amount of air.
- Direct Air: A method of directing supply air directly through the pendant, not a pilot air circuit. Hoists or trolleys that use direct air have larger hoses between the hoist/trolley and the pendant than pilot air controls, and typically provide less ability to feather the hoist.
- Drop Stops: A means to prevent an end truck or trolley from disengaging the beam or rail in the event of an axle or wheel failure.
- Emergency Stop (E-Stop): A red push button that stops all hoist and trolley function when pushed.
- Feathering: The ability to precisely control the speed of the hoist or trolley by varying how far the control pendant lever is depressed or cord control is pulled.
- Festooning: A method for supplying compressed air. This method utilizes loops of hose suspended by a guide wire or enclosed track, which traverses along with the hoist and trolley.
- Filter/Regulator/Lubricator (FRL): An assembly of individual components that is attached on or near the hoist/trolley to filter, regulates the pressure, and lubricates the air supplied to air operated hoists and trolleys.
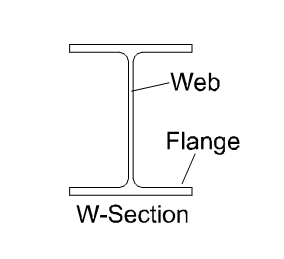
- Flange, Flat: A beam that has flat top and bottom flanges. Also referred to as “W” beams or “H” beams.
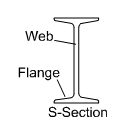
- Flange, Tapered: A beam that has tapered top and bottom flanges. Also referred to as “S” beams.
- Hand Chain (Geared Trolley): The chain that the operator pulls to traverse the load horizontally.
- Hand Chain Drop (Geared Trolley): On drawings in this catalog, hand chain drop is dimension ‘f’ for trolleys. Hand chain drop is a measure of how low the hand chain hangs. For a hoist suspended from a trolley, it is how low the hand chain hangs measured from the bottom of the beam that the trolley rides on.
- Headroom: On drawings in this catalog, headroom is indicated by dimension ‘C’. It is measured when the hoist’s bottom hook is in its uppermost position. For a hook-mounted hoist, headroom is the distance between the saddle of the top and bottom hooks. For a hoist suspended from a trolley, headroom is the distance from the bottom of the beam to the saddle of the bottom hook.
- Hook Parts:

- Hooks, Bullard®: A hook with a positive locking, spring loaded gate.


- Hooks, Inspection: Inspection hooks are suitable for applications where inspection of the internal parts of the hook set is required. The inspection hook uses the standard Harrington hook set and is assembled with high-strength locking fasteners instead of rivets.


- Hooks, SHUR-LOC®: A hook with a positive locking latch that is self-locking and cannot be opened when hook is under load.


- Idle Sheave: Similar to a load sheave except for its location. Idle sheaves can be located in the upper or lower block and guides the chain as it reaves its way through the hook yoke(s).
- Lift: The maximum vertical distance the bottom hook can travel.
- Load Chain: The hoist’s load bearing chain.
- Load Chain, Grade 80: Load chain used only on powered chain hoists, where the grade number indicates the relative strength of the chain for its size (i.e. larger grade numbers indicate stronger chain).
- Load Chain, Nickel Plated: Nickel Plated Load Chain: Load chain with an electroless nickel plating finish to enhance corrosion resistance.
- Load Sheave: The load chain fits into this specially designed sheave which drives the lifting and lowering of the hoist hook. Also referred to as load wheel or pocket wheel.
- Lube-Free: Lube free hoists and trolleys have special features that provide higher durability without supply air lubrication than non-lube free models.
- Manipulator: A unique one-handed control device that is adjacent to the bottom hook and travels up and down with the load hook.
- Minimum Radius for Curve: Defines the sharpest curve of a beam on which the trolley can traverse.
- National Pipe Thread (NPT): A U.S. standard for tapered threads used on threaded pipes and fittings.
- Overload Limiter: A means to prevent the hoist from lifting damaging loads.
- Pendant: This is the hand held push button control device that is attached to the hoist or trolley. The number of buttons can vary dependently upon its uses.
- Pendant or Pull-Cord Drop: On drawings in this catalog, pendant drop is dimension ‘L’ for hoists and trolleys. Pendant drop is a measure of the distance the pendant hangs. For a hoist, it is the distance the pendant hangs from the hoist’s top hook. For a hoist suspended from a trolley, it is the distance the pendant hangs from the bottom of the beam that the trolley rides on. When pendant is specified as “standard to lift”, the bottom of the pendant will hang approximately 4’ above the bottom hook in its lowest position.
Hook Suspended Hoist / Trolley Suspended Hoist

- Pilot Air: A small amount of air bled off from the incoming air supply that is used for the control and actuation of the main hoist valves. Pilot air typically provides finer control (feathering) than direct air control.
- Pounds per Square Inch (PSI): In pneumatic terms, PSI refers to the pressure/force that a compressed air system produces. For hoists and trolleys, it is imperative that the air compressor and compressed air system can produce the required PSI.
- Pull Cord Control: A method of air hoist control that uses cords attached to a lever on the hoist to control direction and speed of the hoist.
- Stainless Steel Load Chain: A stainless steel load chain option for spark resistant applications. Also known as SUS Load Chain.
- Standard, ASME B30.16: “Safety Standard – Overhead Hoists (Underhung).”
- Standard, ASME B30.17: “Safety Standard – Cranes and Monorails (With Underhung Trolley or Bridge).”
- Supply Air: Also known as main air, supply air is the air provided to the hoist/trolley by the compressed air system. Supply air must meet or exceed the PSI and CFM requirements of the hoist/trolley.
- Suspender: A load bearing component designed to connect a hoist to a trolley. Also referred to as “lug”.
- Test Load: The load applied to the hoist to confirm proper operation in accordance with ASME B30.16 test requirements.
- Upper/Lower Limit Lever: A mechanical device that prevents the lower hook from exceeding its’ limits of travel.