CRANE PRODUCT
GLOSSARY
Use our Crane Product Glossary to enhance your understanding of the terminology associated with our crane products.
Crane Product Glossary
- Adjustable Motor Brakes: Electro-mechanical device to control crane deceleration.
- Beam Accessory Kit (“BAK”): All the necessary steel and hardware to fabricate and assemble the bridge beam; this usually consists of braces, mounting plates, end stops, etc.
- Bumpers: A device for reducing horizontal impact when a moving crane or trolley reaches the end of its permitted travel, or when two moving cranes or trolleys come into contact. This device may be attached to the bridge, trolley, or runway stop. Also referred to as buffers.
- Bridge Beam: Traveling beam connected to end trucks; supports the trolley and hoist.
- Capacity: The maximum rated load a hoist is designed to lift. Also referred to as Working Load Limit (WLL) or Safe Working Load (SWL).
- Collectors: Contacting devices for collecting current from the runway or bridge enclosed electrification. Also referred to as “collector shoes”.
- Crane Control Panel: An electrical control box that encloses fusing, transformers, relays, contactors, etc. for the crane system. It controls bridge movement, supplies power to the trolley/hoist, and electrically protects the crane.
- Crane Service Classification Rating: A classification of crane usage and service based on hours of operation and load. See specific product catalog for details on duty service classification.
- Drop Stops: A means to prevent an end truck or trolley from disengaging the beam or rail in the event of an axle or wheel failure.
- Electronic Acceleration Control (EAC): Electronic control for adjusting rate of crane acceleration; also known as electronic soft start.
- Emergency Stop (E-Stop): A red push button that stops all crane functions when pushed.
- Enclosed Conductor Electrification (ECE): Rigid conductor bars that are enclosed to prevent accidental contact. ECE is mounted along the runway structure and/or bridge beam to provide mainline power through collectors to the bridge and/or hoist and trolley.
- End Approach: The maximum horizontal distance the hook can travel.
- End Truck: Load-bearing crane component that supports the bridge beam and consists of a frame, wheels, axles, etc; these can be push, geared or motorized.
- Runway Electrification: Various means to deliver power to the crane system as it travels along the runway. Methods include enclosed conductor electrification or cable festooning.
- Festooning: A method for supplying power and control. This method utilizes loops of cable suspended by a guide wire or enclosed track that traverses along with the crane and/or trolley/hoist.
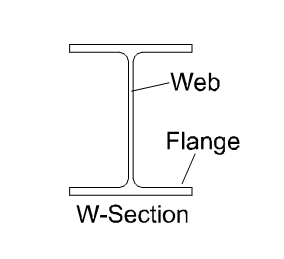
- Flange, Flat: A beam that has flat top and bottom flanges. Also referred to as “W” beams or “H” beams.
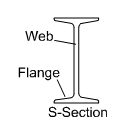
- Flange, Tapered: A beam that has tapered top and bottom flanges. Also referred to as “S” beams.
- Hand Chain (Geared Crane): The chain that the operator pulls to traverse the bridge beam horizontally.
- Hand Chain Drop (Geared Crane): Hand chain drop is a measure of how low the hand chain hangs. For a bottom running crane, it is measured from the bottom of the runway beam. For top running cranes, it is measured from the top of the rail.
- Infinitely Variable, 2-Step: An option available on some VFD controlled cranes. 2 step infinitely variable allows the user to accelerate, then hold any speed between low and high.
- Infinitely Variable, 3-Step: Similar to 2-Step Infinitely Variable but also includes deceleration between high and low speed.
- Mainline Contactor: A method to turn main power to the crane system on and off via crane controls (radio and/or pendant).
- Manual Disconnect Switch: A method to turn main power to the crane system on and off via a manually operated switch. Typically mounted in a bridge control panel.
- National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) Rating: A rating to show the application or environmental conditions enclosures are designed to protect against.
- Pendant: This is the hand held push button control device that is attached to the hoist, trolley, or crane. The number of buttons can vary dependently upon its uses.
- Plug and Play: A crane integration wiring method that terminates all crane wires and trolley hoist festooning via externally mounted plugs on the bridge control panel.
- Power, 3-Phase: A power supply consisting of 3 separate phases of AC Power and a ground, commonly used in industrial applications to power large motors and heavy loads. Common voltages include 208, 230, and 460.
- Rail Sweeps: Devices designed to clear obstructions from wheel running surface.
- Runway Beam: Stationary beams that support crane and load; commonly fabricated from S or W beams or patented track.
- Span: Dimension from the center line of one runway beam to the center line of the other runway beam.
- Standard, ASME B30.2: “Safety Standard – Overhead and Gantry Cranes (Top Running Bridge, Single or Multiple Girder, Top Running Trolley Hoists).”
- Standard, ASME B30.16: “Safety Standard – Overhead Hoists (Underhung).”
- Standard, ASME B30.17: “Safety Standard – Cranes and Monorails (With Underhung Trolley or Bridge).”
- Standard, OSHA Section 1910.179 of Title 29: “Occupational Safety and Health Regulations – Overhead and Gantry Cranes”.
- System Max Wheel Load: Maximum load exerted on runway beams for a crane loaded to its rated capacity. It occurs when trolley/hoist is located at its maximum end approach and includes an allowance for vertical inertial forces associated with electric hoists. This value is expressed as pounds per wheel for top running or pounds per pair of wheels for under hung.
- Thermal Protection: A method to protect electric motors from damage due to over-current or overheating.
- Top Running: Crane type that travels on top of rail or bar attached to runway beams.
- Travel Limit Switches: An electro-mechanical device that prevents the crane from exceeding its’ horizontal limits of travel.
- Underhung: Crane type that travels on the lower flange of the runway beams.
- Variable Frequency Drive (VFD): Also known as an inverter. An electronic device that controls the voltage and frequency to an electric motor to control speed and/or torque.